LeetCode Hot 100 (8) 链表 (二)
# 21. 合并两个有序链表 (opens new window)
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例 1:
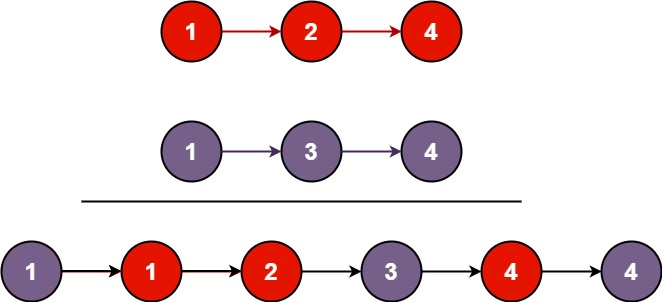
输入:l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]
2
示例 2:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = []
输出:[]
2
示例 3:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = [0]
输出:[0]
2
提示:
- 两个链表的节点数目范围是 [0, 50]
- -100 <= Node.val <= 100
- l1 和 l2 均按 非递减顺序 排列
思路:
有递归法和迭代法两种,这里用迭代法,就是新建一个虚拟头节点然后每次在后面脸上比较小的那个节点。
代码:
C++代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) {
ListNode* dummyhead = new ListNode(0), *cur = dummyhead;
while(list1!=nullptr&&list2!=nullptr) {
if(list1->val<=list2->val) {
cur->next = list1;
list1 = list1->next;
cur = cur->next;
} else {
cur->next = list2;
list2 = list2->next;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
if(list1!=nullptr) cur->next = list1;
else if(list2!=nullptr) cur->next = list2;
return dummyhead->next;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
Go代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func mergeTwoLists(list1 *ListNode, list2 *ListNode) *ListNode {
dummyhead := new(ListNode)
cur := new(ListNode)
cur = dummyhead
for list1!=nil && list2!=nil {
if list1.Val<=list2.Val {
cur.Next = list1
cur = cur.Next
list1 = list1.Next
} else {
cur.Next = list2
cur = cur.Next
list2 = list2.Next
}
}
if list1!=nil {
cur.Next = list1
} else if list2!=nil {
cur.Next = list2
}
return dummyhead.Next
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
# 2. 两数相加 (opens new window)
题目:
给你两个 非空 的链表,表示两个非负的整数。它们每位数字都是按照 逆序 的方式存储的,并且每个节点只能存储 一位 数字。
请你将两个数相加,并以相同形式返回一个表示和的链表。
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数都不会以 0 开头。
示例 1:
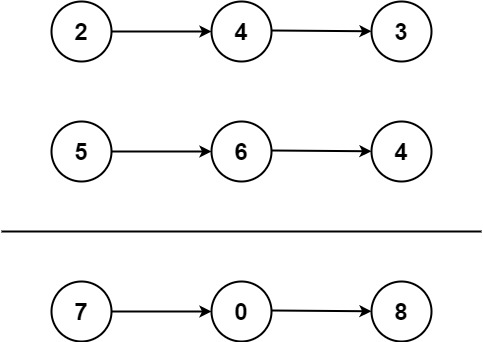
输入:l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4]
输出:[7,0,8]
解释:342 + 465 = 807.
2
3
示例 2:
输入:l1 = [0], l2 = [0]
输出:[0]
2
示例 3:
输入:l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9]
输出:[8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]
2
提示:
- 每个链表中的节点数在范围 [1, 100] 内
- 0 <= Node.val <= 9
- 题目数据保证列表表示的数字不含前导零
思路:
新建节点,按照加法逻辑进行模拟。
代码:
C++代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode* dummyhead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode* cur = dummyhead;
int t = 0;
while(l1!=nullptr||l2!=nullptr) {
if(l1!=nullptr) {
t += l1->val;
l1 = l1->next;
}
if(l2!=nullptr) {
t += l2->val;
l2 = l2->next;
}
ListNode* temp = new ListNode(t%10);
cur -> next = temp;
cur = cur->next;
t = t/10;
}
if(t) {
ListNode* temp = new ListNode(t%10);
cur -> next = temp;
}
return dummyhead->next;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
Go代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func addTwoNumbers(l1 *ListNode, l2 *ListNode) *ListNode {
dummyhead := new(ListNode)
cur := new(ListNode)
cur = dummyhead
t := 0
for l1!=nil || l2 !=nil {
if l1!=nil {
t += l1.Val
l1 = l1.Next
}
if l2!=nil {
t += l2.Val
l2 = l2.Next
}
temp := new(ListNode)
temp.Val = t%10
cur.Next = temp
cur = cur.Next
t/=10
}
if t>0 {
temp := new(ListNode)
temp.Val = t
cur.Next = temp
}
return dummyhead.Next
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
# 19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点 (opens new window)
题目:
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
示例 1:
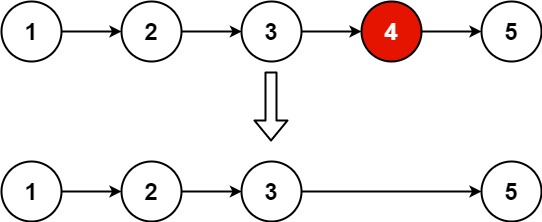
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2
输出:[1,2,3,5]
2
示例 2:
输入:head = [1], n = 1
输出:[]
2
示例 3:
输入:head = [1,2], n = 1
输出:[1]
2
提示:
- 链表中结点的数目为 sz
- 1 <= sz <= 30
- 0 <= Node.val <= 100
- 1 <= n <= sz
进阶:你能尝试使用一趟扫描实现吗?
思路:
用快慢指针,快指针先走n步,然后快慢指针同时走,这样当快的到终点时,慢的到了要删除的位置。
代码:
C++代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode* dummyhead = new ListNode(0,head);
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* slow = dummyhead;
while(n--) {
fast = fast->next;
}
while(fast!=nullptr) {
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
slow->next = slow->next->next;
ListNode* res = dummyhead->next;
delete dummyhead;
return res;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
Go代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func removeNthFromEnd(head *ListNode, n int) *ListNode {
dummyhead := new(ListNode)
dummyhead.Next = head
fast := new(ListNode)
fast = head
slow := new(ListNode)
slow = dummyhead
for n>0 {
n--
fast = fast.Next
}
for fast!=nil {
fast = fast.Next
slow = slow.Next
}
slow.Next = slow.Next.Next
return dummyhead.Next
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
# 24. 两两交换链表中的节点 (opens new window)
题目:
给你一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后链表的头节点。你必须在不修改节点内部的值的情况下完成本题(即,只能进行节点交换)。
示例 1:
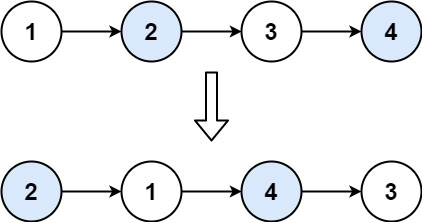
输入:head = [1,2,3,4]
输出:[2,1,4,3]
2
示例 2:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
2
示例 3:
输入:head = [1]
输出:[1]
2
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目在范围 [0, 100] 内
- 0 <= Node.val <= 100
思路:
构建三个节点 pre,cur,nxt进行遍历
代码:
C++代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* dummyhead = new ListNode(0);
dummyhead->next = head;
ListNode* pre = dummyhead;
ListNode* cur = head;
if(head==nullptr) return nullptr;
ListNode* nxt = head->next;
while(cur!=nullptr && nxt!=nullptr) {
cur->next = nxt->next;
nxt->next = cur;
pre->next = nxt;
pre = cur;
cur = cur->next;
if(cur!=nullptr) {
nxt = cur->next;
}
}
return dummyhead->next;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
Go代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func swapPairs(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
dummyhead := new(ListNode)
dummyhead.Next = head
pre := new(ListNode)
pre = dummyhead
cur := new(ListNode)
cur = head
if head==nil {
return nil
}
nxt := new(ListNode)
nxt = head.Next
for cur!=nil && nxt!=nil {
cur.Next = nxt.Next
nxt.Next = cur
pre.Next = nxt
pre = cur
cur = cur.Next
if cur!=nil {
nxt = cur.Next
}
}
return dummyhead.Next
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
# 25. K 个一组翻转链表 (opens new window)
题目:
给你链表的头节点 head ,每 k 个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回修改后的链表。
k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。如果节点总数不是 k 的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际进行节点交换。
示例 1:
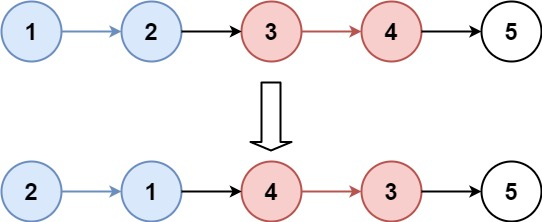
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2
输出:[2,1,4,3,5]
2
示例 2:
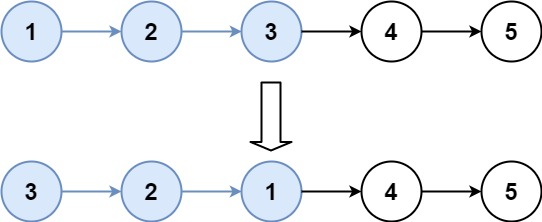
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 3
输出:[3,2,1,4,5]
2
提示:
- 链表中的节点数目为 n
- 1 <= k <= n <= 5000
- 0 <= Node.val <= 1000
进阶:你可以设计一个只用 O(1) 额外内存空间的算法解决此问题吗?
思路:
不进阶的化可以用一个栈来实现,下面是进阶的代码,主要是模拟的过程比较复杂
代码:
C++代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {
int n = 0;
for(ListNode* cur = head;cur!=nullptr;cur=cur->next) {
n++;
}
ListNode* dummyhead = new ListNode(0,head);
ListNode* p0 = dummyhead;
ListNode* pre = nullptr;
ListNode* cur = head;
for(;n>=k;n-=k) {
for(int i=0;i<k;i++) {
ListNode* nxt = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = nxt;
}
ListNode* temp = p0->next;
p0->next->next = cur;
p0->next = pre;
p0 = temp;
}
return dummyhead->next;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
Go代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func reverseKGroup(head *ListNode, k int) *ListNode {
dummyhead := new(ListNode)
dummyhead.Next = head
n := 0
for cur:=head;cur!=nil;cur=cur.Next {
n++
}
p0 := dummyhead
pre := new(ListNode)
cur := head
for ;n>=k;n-=k {
for i:=0;i<k;i++ {
nxt := cur.Next
cur.Next = pre
pre = cur
cur = nxt
}
temp := p0.Next
p0.Next.Next = cur
p0.Next = pre
p0 = temp
}
return dummyhead.Next
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
